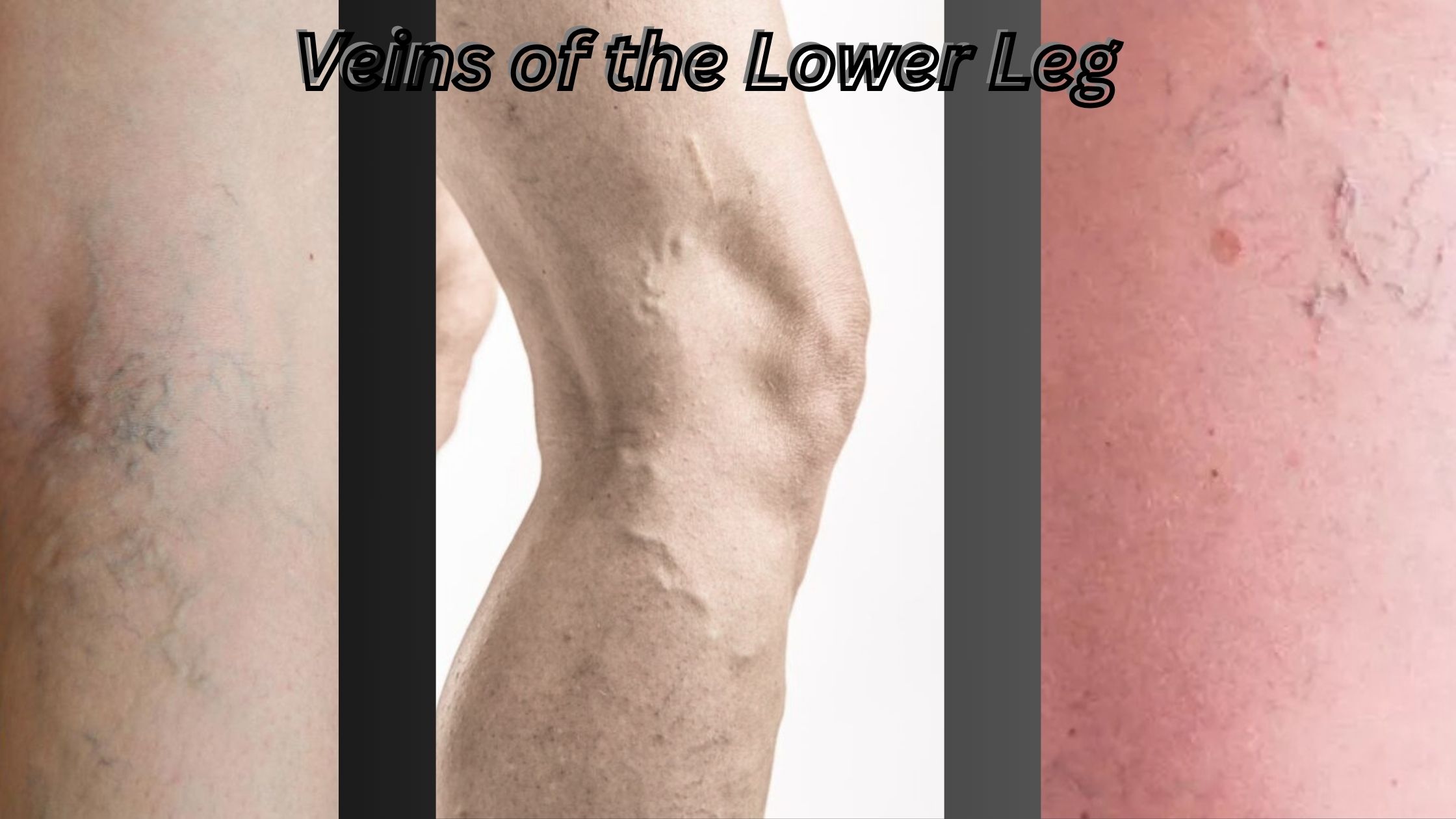
The lower leg veins play an important role in the body’s circulation system and carrying deoxygenated blood back to the heart. These veins, including great saphenous vein (GSV), small saphenous veins (SSV), and deep veins like posterior tibial and peroneal veins, are necessary to maintain healthy blood flow.
However, problems such as varicose vein leg pain, pain in the bottom of leg and foot, and discomfort where the vein in thigh hurts can signal underlying venous conditions. This article discusses the anatomy of the lower veins of the legs, the general causes of pain, symptoms and treatment options, and provides a comprehensive guide to those who experience discomfort.
Anatomy of the Veins of the Lower Leg
The lower leg has a complex network of veins which is divided into superficial and deep systems. Superficial veins, such as great and small saphenous veins, are more located near the skin and more sensitive to conditions like varicose veins. Deep veins, including anterior tibial, posterior tibial and peroneal veins, are located within the muscle compartments and handle most of the blood return from the legs. These veins work together with valves that prevent backflow, making sure that blood flow efficiently towards the heart.
When the lower leg veins are affected, it can cause symptoms such as swelling, pain or pain in the bottom of leg and foot. Conditions affecting these veins are often caused by valve malfunction, blood clots, increased pressure in venous mechanisms, causing discomfort in the area of the thigh, where a vein in thigh hurts.
Common Causes of Pain in the Veins of the Lower Leg
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are increased, folded veins that often appear in the lower part of the legs due to weak vein walls or defective valves. This condition, known for causing varicose vein leg pain, is caused by blood pooling in the veins, which increases the pressure. Its symptoms include pain, heaviness and appearance of bulging veins. Standing/sitting for a long time, pregnancy, obesity and heredity are its common risk factor.
DVT
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when in one of the deep veins, often in the lower leg or thigh, a blood clot is formed. This can cause severe pain, swelling and warmth in the affected area. If vein in thigh hurts, it can be a sign of DVT, which is a serious condition and the risk of pulmonary embolism requires immediate therapy, where the clot reaches the lungs.
CVI
CVI arises when the veins feel difficulty in returning the blood to the heart, causing blood to pooling in the lower legs. This can also cause pain in the bottom of leg and foot, swelling, skin changes and ulcer in severe cases. CVI often develops from untreated varicose veins or previous DVT.
Superficial Thrombophlebitis
This condition involves inflammation and clotting in a superficial vein, which often causes local pain, redness and swelling. Although it is less serious than DVT, it can cause discomfort in the veins of the lower leg.
Symptoms to Watch For
Pain in the veins of the lower leg can manifest in various ways, depending on the underlying condition. Common symptoms include:
- Aching or throbbing
- Swelling
- Pain in the bottom of leg and foot
- Tenderness or warmth
- Skin changes
If you feel symptoms like sudden swelling, severe pain, shortness of breath or chest pain, seek medical help immediately, as they may be a sign of life -threatening conditions like DVT.
Diagnosis of Venous Conditions
To diagnose lower leg veins problems usually include a combination of physical tests and imaging tests. A health service provider can do the following:
- Perform a physical exam: Checking visible varicose veins, swelling or skin changes.
- Use ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound is usually used to assess blood flow and detect dysfunction of clots or valves.
- Order additional tests: In cases of suspected DVT, D-dimmer blood test or venography can be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications, especially for conditions causing pain in the bottom of leg and foot or when a vein in thigh hurts.
Treatment Options for Vein-Related Pain
Lifestyle Changes
In mild cases of varicose vein leg pain or discomfort in the veins of the lower leg, lifestyle changes can be relieved. These include:
- Exercise
- Weight management
- Elevating legs
- Avoiding prolonged sitting/standing
Compression Therapy
CS plays an important role in treating venous problems. These clothes put light pressure on the legs, promote blood flow and reduce swelling and varicose vein leg pain.
Medical Interventions
For more severe cases, medical procedures may be necessary:
- Sclerotherapy
- Endovenous ablation (EVLA)
- Vein stripping
- Anticoagulants
Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, home remedies can help manage symptoms:
- Cold or warm compresses: Applying warm compress can varicose vein leg pain, while cold compress can reduce inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: OTC medicine like ibuprofen can alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Herbal supplements: Few studies show that horse chestnut extracts can improve CVI symptoms, although consults a doctor before use.
Prevention Tips for Healthy Veins
Preventing issues with the veins of the lower leg involves adopting habits that support circulation:
- Stay active
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Stay hydrated
- Wear loose clothing
When to See a Doctor
While mild discomfort in the veins of the lower leg can often be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Seek help if you experience:
- Sudden or severe swelling in the leg or thigh
- Intense pain, especially if a vein in thigh hurts or the area feels warm
- Skin changes, such as ulcers or darkening near the ankles
- Symptoms of DVT, such as unilateral leg swelling or pain that worsens with movement
Conclusion
The veins of the lower leg are vital for healthy circulation, but conditions like varicose veins, DVT, and chronic venous insufficiency can lead to discomfort, including varicose vein leg pain, pain in the bottom of leg and foot, or cases where a vein in thigh hurts. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to manage these issues effectively. By adopting lifestyle changes, using compression therapy, or seeking medical interventions, you can alleviate pain and prevent complications. If you suspect a serious condition, consult a healthcare provider promptly to ensure the best outcomes for your vein health.