- admin
- 0 Comments
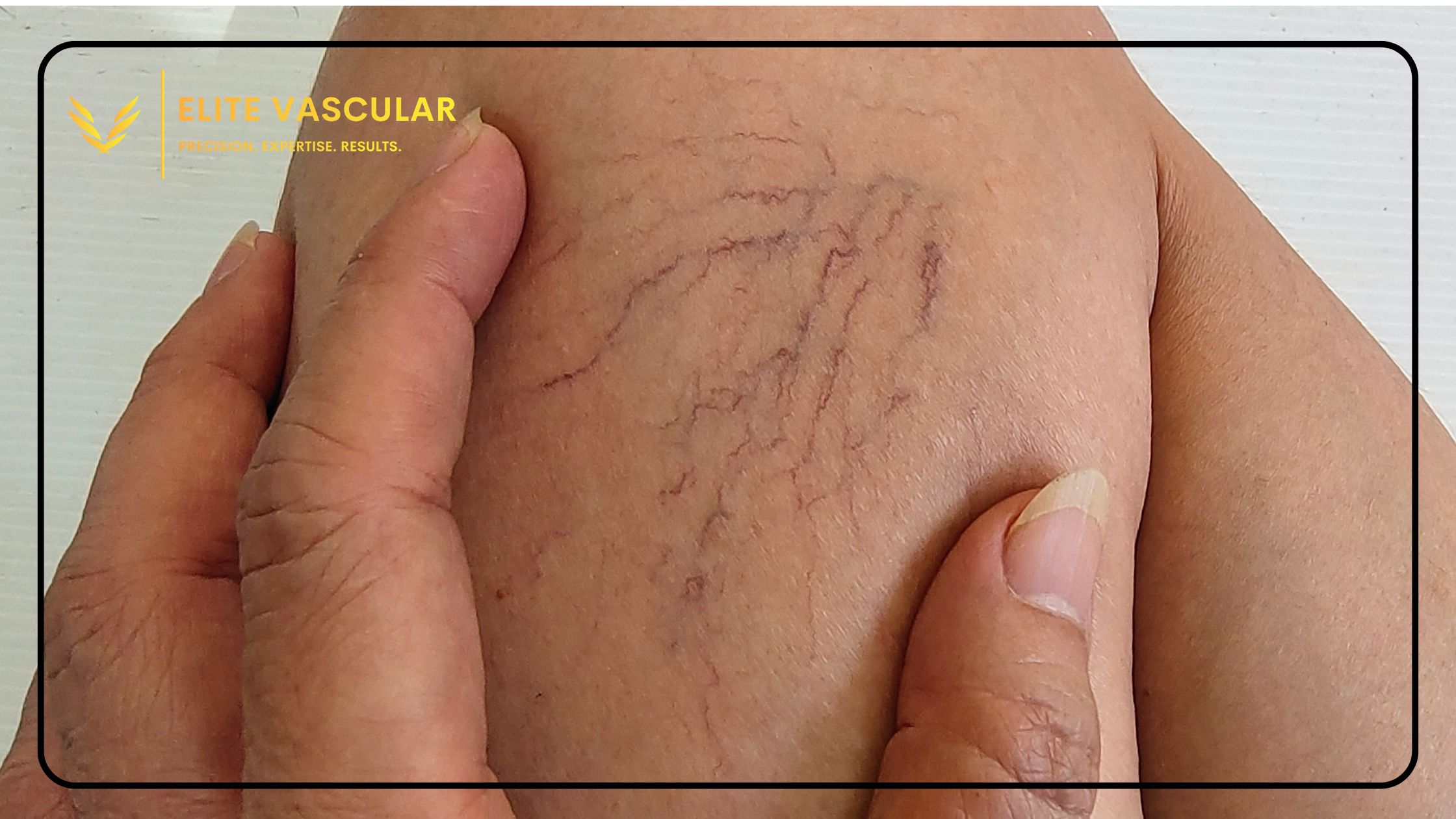
What Are Reticular Veins?
While varicose and spider veins are well-known, reticular veins may not be. They are smaller than varicose veins, whose diameter is about 2 mm. They don’t even get out of the skin like varicose veins. The color of reticular and varicose veins is the same (blue or purple). They also appear in many similar parts of the body. Common areas include the inner and previous part of the thigh as well as the lower legs and ankles. They sometimes appear on the face, although it’s more prevalent with spider veins. Reticular veins can sometimes feed into spider veins. That’s why they are also known as feeder veins. When they do this, they provide additional blood for spider veins. Under such circumstances, removing reticular veins can also help to eliminate spider veins.
Symptoms of Reticular Vein
Reticular veins are sometimes known as ‘blue veins’ or ‘feeder veins’. This disorder develops when dilated veins enable outgoing blood to move backward. Due to this increased pressure the veins start expanding. Additionally, they have the ability to discolor the skin and cause green or blue streaks beneath it, giving an aesthetically unpleasant marbled appearance. Reticular veins may or may not be identified without the aid of magnification. It is important to identify and treat reticular veins to effectively control spider veins. Reticular veins can cause pain and discomfort in the surrounding areas. They may sometimes cause itching or burning. In rare circumstances, the presence of reticular veins may indicate a backup of blood in the deeper tissues of the leg. However, in most situations, reticular veins are only a cosmetic issue that can be addressed quickly.
Reticular veins common symptoms include:
- Itching or irritation, pain or warmth
- Burning, common unease in the area
- Tiredness and heaviness
- Blue, green, red, or purplish spider-like under-skin appearance
- Standing for long durations causes leg pain and swelling
Various treatment options for Reticular Veins
If you are still experiencing discomfort by reticular or varicose veins or want cosmetic treatment, see a vein specialist. The size, location of your vein and venous insufficiency will greatly impact your treatment options. The medical treatment of existing reticular veins often prevents the formation of spider veins. Treatment of reticular veins can also cause disappear nearby spider veins. Sclerotherapy improves blood circulation by closing damaged, visible veins. This may slow or stop the production of new reticular veins, but new visible veins are likely to form. Additional sclerotherapy sessions can help maintain a improved appearance.
Sclerotherapy (ultrasound guided)
Sclerotherapy, when done rightly with proper technique, is the most successful way to treat reticular veins and telangiectases.
Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy includes injecting a sclerosing agent into the vein. The inner walls of the vein collapses, from which it shuts down. Blood naturally flows into other healthy veins. During a few months, the body reabsorbs the old vein, which eventually disappears.
Varithena
At EliteVs, we use varithena for this sclerotherapy treatment. Its microfoam is particularly well tolerated by individuals undergoing sclerotherapy, and the procedure requires no anesthetic. Patients receiving the therapy report brighter, smoother skin in areas where blue veins were previously present. Treating reticular veins reduces the risk of developing spider veins in those areas.
What causes Reticular Veins?
Reticular veins develop when blood is deposited in the veins of the foot instead of going to the heart, like form spider and varicose veins. Normally functioning veins return the blood from different areas of the body to the heart. Blood flows backwards from the heart when the vein valve failure and assembles downwards towards the legs and feet. Because they may feed in spider veins and provide blood source for blood stranded in spider veins, reticular veins are also known as feeder veins. In this case, removal reticular veins can also reduce the visibility of spider veins.
Due to this malfunction, the reticular veins may become more bulging or swollen and cause discomfort when standing for long periods of time.
Some causes that may contribute to the formation of reticular veins are:
- Age: As we age, veins lose their suppleness and function weaken
- Heredity: If your family member has reticular veins or another vein disorder, you may be at risk for developing the same condition
- Obesity: Try to be in shape always, excess weight puts pressure on veins in the legs
- Pregnancy: As the fetus grows and blood volume increases in the body, the veins can be large
- Additional health issues: Abdomen tumors and prolonged constipation can put pressure on the stomach and legs
How long until my reticular veins look better after treatment?
Results take time because the treated veins are slowly reabsorbed by your body after treatment. The amount of time required will be determined by the severity and size of your reticular veins as well as your ability to follow care instructions. Most of patients undergoing treatment for reticular veins see their final results approximately 6 months after treatment.
When to See a Doctor for Reticular Veins?
If you are experiencing any kind of vein problem, consult a doctor. See a doctor for medical help if you experience the following:
- Pain or discomfort in or around veins
- Bleeding veins, Ulcers around veins
- Doctor will diagnose your vein problem with a vascular screening
- Doctor will treat any damaged veins
- Doctor will provide treatment for cosmetically displeasing veins
Seek expert advice for reticular vein in NJ
Ask our board certified vein specialist Nirman Tulsyan to resolve the reticular vein issue. Book an appointment by visiting our website or call us at +1-973-975-4447 in Clifton, NJ.