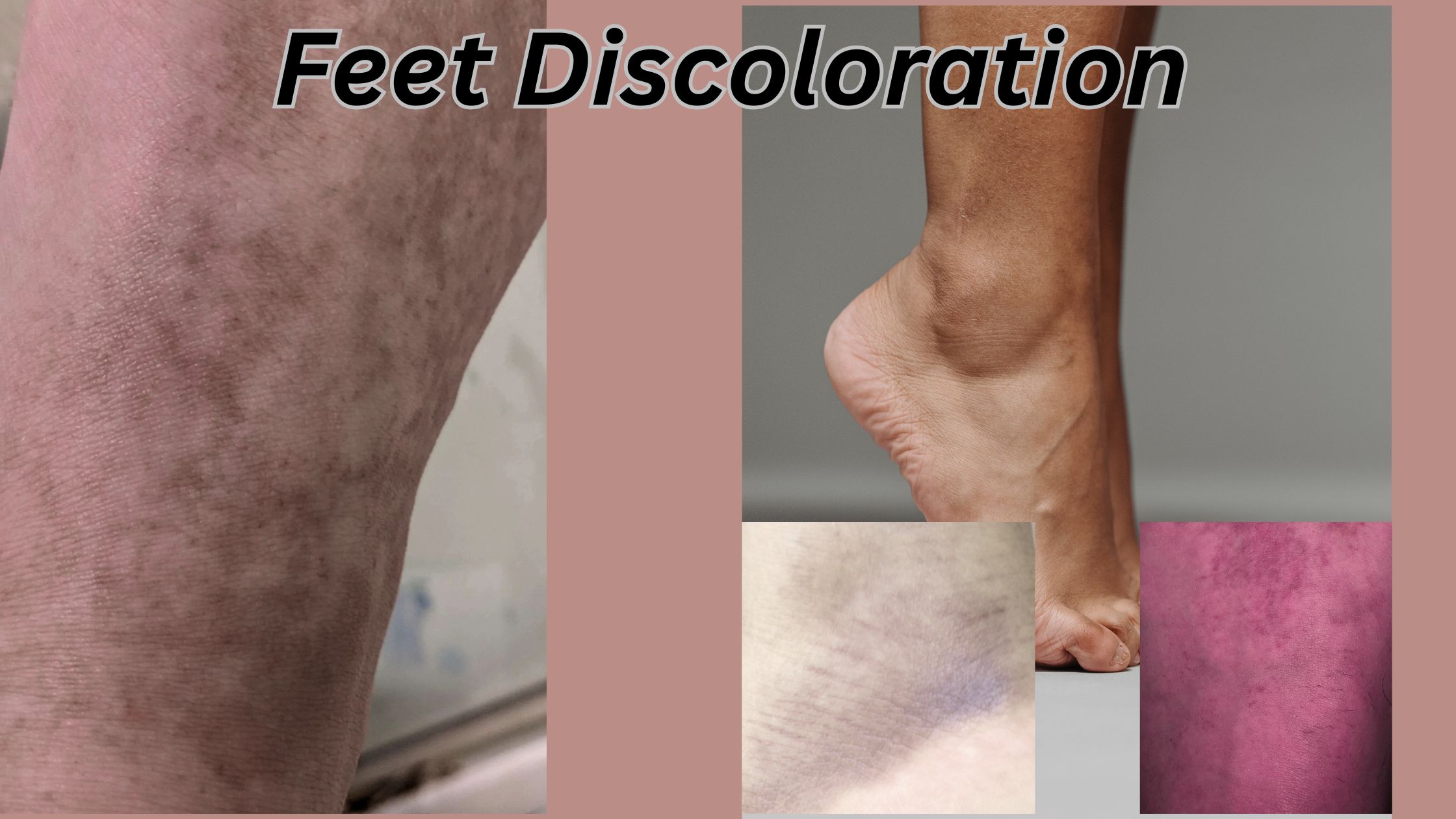
Feet discoloration is a common concern that can manifest in various forms, such as a brown spot on my foot, black mark on heel of foot, black patches on your feet, black patches on my feet. These changes in skin color can be alarming, prompting questions about their causes and potential health implications.
While some cases are benign, other underlying medical conditions may indicate that require attention. This article explores the causes behind feet discoloration, its symptoms and practical steps to address it, and provides a comprehensive guide to understand and manage this problem.
What Causes Feet Discoloration?
Feet discoloration can result from a wide range of factors, from harmless skin changes to more serious health conditions. Some common causes are given below:
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, is produced in certain areas. Brown spot on your foot or black patches on your feet due to this condition. Exposure of sunlight, friction from tight shoes or repeated pressure on the feet can lead to hyperpigmentation, especially on the heels or soles. For example, a black mark on the heel of your foot might develop from constant rubbing against footwear.
Bruising or Trauma
Physical trauma, such as an injury to your toe or falling something heavy on your foot, can cause injury appearing in the form of black spots on the bottom of the feet or black spots in other places. These marks usually fade over time because the body is cured. However, a medical examination is required to detect problems such as blood clotting when injuries continuously or without any reason.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections such as athlete foot can change the skin color, especially black patches on your feet or black spots on the soles. These infections thrive in a warm, moist environment, such as sweaty shoes or public shower. Along with changing color (discoloration), symptoms may include itching, crust formation or foul odor. OTC antifungal remedies can often cure light cases, but a prescription drug may be required for severe infection.
Poor Circulation
Poor blood circulation, which is often associated with conditions like diabetes or PAD, can cause black spots on the bottom of the feet or a black mark on the heel of foot. The skin discoloration can be bad due to low blood flow, numbness, or slow-healing wounds. If you see these symptoms immediately consult a healthcare provider, as they may be a sign of a serious vascular problem.
Skin Cancer
In rare cases, brown spots or black spots on your feet may be a sign of skin cancer, such as melanoma. Melanomas on the feet often appear as asymmetrical, irregularly delimited spots with several colors (brown, black or red). If a spot changes in size, shape or color, or if blood out of it or itching, check with a dermatologist immediately.
Medication Side Effects
Some medications, such as chemotherapy drugs or anti-malaria drugs, may worsen the skin discoloration as side effects. It may appear as black spots on the feet bottom, soles or brown spots on the foot. If you suspect a medication is causing discoloration, talk to your doctor about this, but do not stop taking medications prescribed without the doctor’s guidance.
Other Medical Conditions
Skin color may be bad due to conditions like Addison disease, liver diseases or kidney problems, including black patches on your feet. These systemic conditions are often present with additional symptoms like fatigue, weight loss or jaundice, and require medical diagnosis and management.
Recognizing Symptoms of Feet Discoloration
The problem of feet discoloration can vary and it may also have other symptoms, which depend on the cause. Common symptoms include:
- Brown Spot on Your Foot: Single, flat or slightly raised spot that can be uniform or irregular in color.
- Black Mark on Heel of Foot: The black area on the heel, which is often caused by friction, trauma or hyperpigmentation.
- Black Patches on Your Feet: Color changes (discoloration) in large area, which are probably associated with infection, blood circulation problems or systemic conditions.
- Black Spots on the Bottom of the Feet: Small, scattered spots that may be caused by injury, fungal infection or melanoma.
Additional symptoms such as itching, pain, swelling, heat or skin texture changes should be noted. If skin discoloration persists, worsened or systemic symptoms like fever or fatigue appear, consult a doctor immediately.
When to See a Doctor
Although black spot on your foot may be harmless, or on the foot heel, some symptoms demand professional assessment:
- Color change (discoloration) that spreads, comes in appearance changes, or doesn’t fade over time.
- Pain, swelling or heat in the affected area.
- Open wound, ulcers or slow healing wounds on the feet.
- Systemic symptoms, such as fatigue, loss of weight or fever.
- Family history of skin cancer or other serious conditions.
A dermatologist or podiatrist can perform physical testing, review your medical history, and if necessary, testing such as skin biopsy, blood work or imaging to determine the cause.
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
The treatment of feet discoloration depends on its underlying cause. Here are some common measures:
Topical Treatments
For hyperpigmentation or fungal infection, OTC or prescription creams may be helpful. Hydroquinone or retinoids can light brown spots on your foot, while antifungal creams can address black patches caused by infections.
Improved Footwear
Wearing good fittings, breathable shoes can reduce friction and don’t (prevent) have black spots on your foot heel or black spots on the bottom of the feet. Orthotic inserts can also help to evenly distribute the pressure.
Good Foot Hygiene
Wash your feet regularly and drying well can prevent fungal infection which produces black spots on your feet. Use moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and avoids cracking, which can reduce skin color.
Medical Interventions
For serious conditions such as poor blood circulation or skin cancer, medical intervention may be necessary. This may include vascular treatment, removing cancer wounds by surgery or managing built-in systemic diseases.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy diet, stay active and managing chronic diseases like diabetes can improve blood communication and reduce the risk of changes in skin color. Avoid prolonged sun exposure on your feet and use sunscreen to prevent hyperpigmentation.
Home Remedies for Mild Discoloration
For light changes in the color of legs, such as brown spots on the foot due to hyperpigmentation, home treatment can be helpful:
- Lemon Juice’s natural bleaching properties can lighten dark spots. Apply diluted lemon juice to the affected area for 10 minutes, then rinse.
- Aloe vera well known for its soothing and skin-lightening effects, aloe vera gel can be applied daily to reduce discoloration.
- Baking soda scrub can remove dead skin and lighten a black mark on the heel of your foot.
Always test home remedies on a small area first to avoid irritation, and discontinue use if discomfort occurs.
Conclusion
Feet discoloration, whether it’s a brown spot on your foot, a black mark on the heel of your foot, black patches on your feet, or black spots on the bottom of the feet, can stem from various causes, ranging from benign to serious. By understanding the potential triggers and symptoms, you can take proactive steps to address the issue. Practice good foot hygiene, wear appropriate footwear, and seek medical advice if discoloration persists or worsens. With the right care and attention, you can keep your feet healthy and free from unwanted marks.