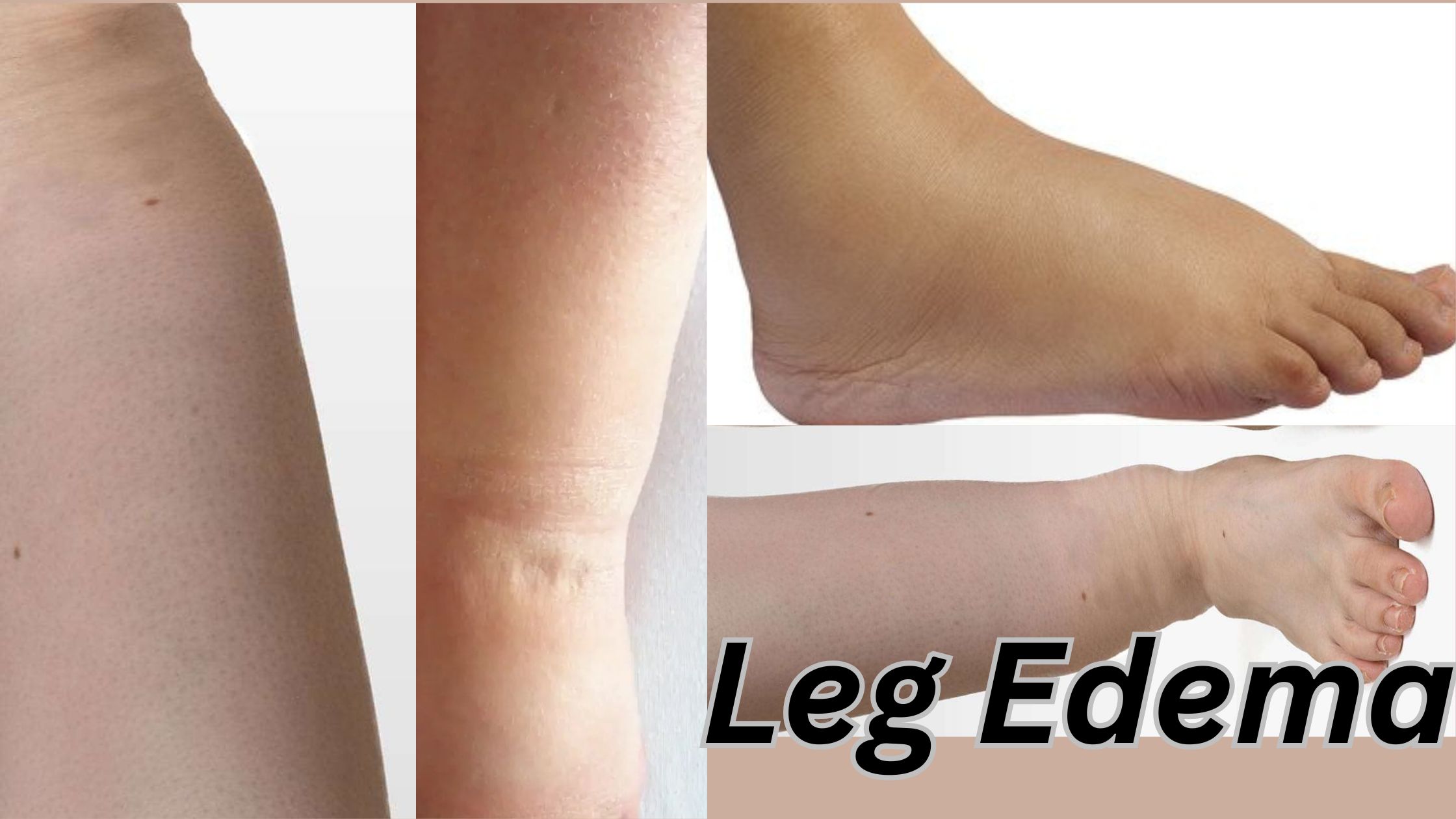
Inflammation in the left leg, also called left leg edema, is a common problem which many people ever experience in their lives. While mild swelling can be harmless – often from standing or sitting for too long, this can sometimes even indicate a serious built-in health condition. Left leg edema, or swelling, harmless or any serious illness may be indicated. Light swelling often occurs from sitting/standing for too long, eating more salt or minor injuries and usually improves with rest and elevation.
However, if inflammation occurs suddenly, just affects one leg, and comes with pain, heat or redness, this could be a sign of dangerous blood clots (DVT). Other warning signs include breathing distress, chest pain or swelling which does not fix even after resting – these may be a sign of heart, kidney or liver problems. If you see these symptoms, meet a doctor immediately to avoid hazardous conditions for life.
If you’re worried about your left leg swelling, this article will help you understand:
- Common causes of left leg edema
- Warning signs that indicate a serious problem
- When to see a doctor
- Home remedies and prevention tips
What Is Left Leg Edema?
Edema refers to fluid buildup in body tissues, leading to swelling. When this happens in the left leg, it may appear puffy, feel heavy, or leave an indentation when pressed (known as pitting edema).
Common edema in the legs causes
Mild Causes (Usually Not Serious)
- Prolonged sitting or standing. For example, long flights, desk jobs
- High salt intake
- Pregnancy (During pregnancy period increased pressure on leg veins)
- Injury or strain (sprains, muscle tears)
Serious Causes (Need Medical Attention Immediately)
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) – A blood clot in the leg, which can be life-threatening if it travels to the lungs also called pulmonary embolism.
- Heart failure – Due to weak heart functioning results poor blood circulation and fluid deposited.
- Kidney disease – Fluid retention is due to malfunction in the kidney function.
- Liver disease – Low levels of protein swells the legs and stomach.
- Lymphedema – Interruption (blockage) in the lymphatic system, often after surgery or infection.
How to Tell If Left Leg Edema Is Serious?
All inflammation isn’t dangerous, but some red flags mean you should meet a doctor immediately.
1. Sudden, Severe Swelling (Especially in One Leg)
If there is only inflammation in your left leg (not in both), this could be a sign of deep vein thrombosis (blood clot).
Various warning signs of DVT:
- Pain or tenderness in the calf or thigh
- Warmth and redness over the swollen area
- Swelling that worsens over hours/days
If you have breathing difficulty or chest pains (this may mean that clot has moved to the lungs) take emergency care ASAP.
2. Swelling with Other Symptoms
Heart-related edema:
- Shortness of breath, Fatigue
- Swelling in both legs and abdomen
Kidney-related edema:
Puffy face, especially in the morning
- Reduced urination, Foamy urine
Liver-related edema:
- Yellow skin (jaundice), Abdominal swelling (ascites)
3. Non-Pitting Edema (there is no mark on pressing)
If pressing your swollen leg does not cause any temporary mark, this could be lymphedema or thyroid disease.
- Lymphedema is often after cancer treatment or infection.
4. Skin Changes & Ulcers
- Discoloration (red, purple, or shiny skin)
- Open sores or wounds that won’t heal
- Hard, tight skin (fibrosis in chronic cases)
5. Swelling that Doesn’t Improve with Elevation or Rest
- Light swelling from standing/sitting for too long usually fixes by lifting the foot or walking.
- If selling persists despite resting, it could be a sign of a big problem like heart or kidney disease.
When to See a Doctor (edema on legs)?
See a doctor if:
- Only one leg is swollen (possible DVT)
- Swelling is painful, red or warm
- You have shortness of breath or chest pain
- Swelling worsens over time
- You notice sudden weight gain (fluid retention)
Seek emergency care if:
- You are having difficulty breathing chest pain or breathing (possibly pulmonary embolism)
- Your foot is cold, pale or numb (could means arterial blocked)
How left leg pain and swelling Diagnosed?
Doctors may perform:
- Ultrasound (to check for blood clots)
- Blood tests (for heart, kidney, or liver function)
- X-rays or CT scans (if infection or tumor is suspected)
- Echocardiogram (if heart failure is possible)
Home Remedies for Mild Leg Swelling
If your swelling is not serious, try these natural relief methods:
Elevate Your Legs: Lie down and elevate your legs above heart level for 20-30 minutes, 2-3 times daily.
Reduce Salt Intake: The problem of fluid retention from more salt becomes even worse. Avoid processed foods, canned soups and salty snacks.
Wear Compression Stockings: Compression stocking improve circulation and reduce swelling. Consult with your healthcare provider for best result.
Stay Active (Avoid Sitting Too Long)
- If you have desk job then take a walk every hour, avoid prolong sitting/standing.
- Try ankle pumps (move feet up and down) to boost blood flow.
Massage & Cold Compress
- Massaging light towards the heart helps to drain excess fluid.
- A cold pack can reduce inflammation from injury.
Natural Diuretics (Water Pills Alternatives)
- Dandelion tea, parsley and cucumber help flush out excess fluid.
Preventing Left Leg Edema
- Exercise regularly like walking, swimming, yoga
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay hydrated with proper water consumption (helps kidneys flush out toxins)
- Avoid tight clothing that restricts blood flow
Notable Insights:
- One-leg swelling + pain = Possible DVT (blood clot)
- Swelling + shortness of breath = Emergency
- Chronic swelling may indicate heart, kidney or liver disease
- Home remedies help mild cases, but persistent swelling needs a doctor
Final Thoughts
Left leg edema can range from a minor issue to a life-threatening condition. While occasional swelling from sitting too long is normal, sudden, painful, or one-sided swelling needs urgent medical attention. If you’re unsure, always consult a healthcare provider to rule out serious conditions. Early detection can save lives.