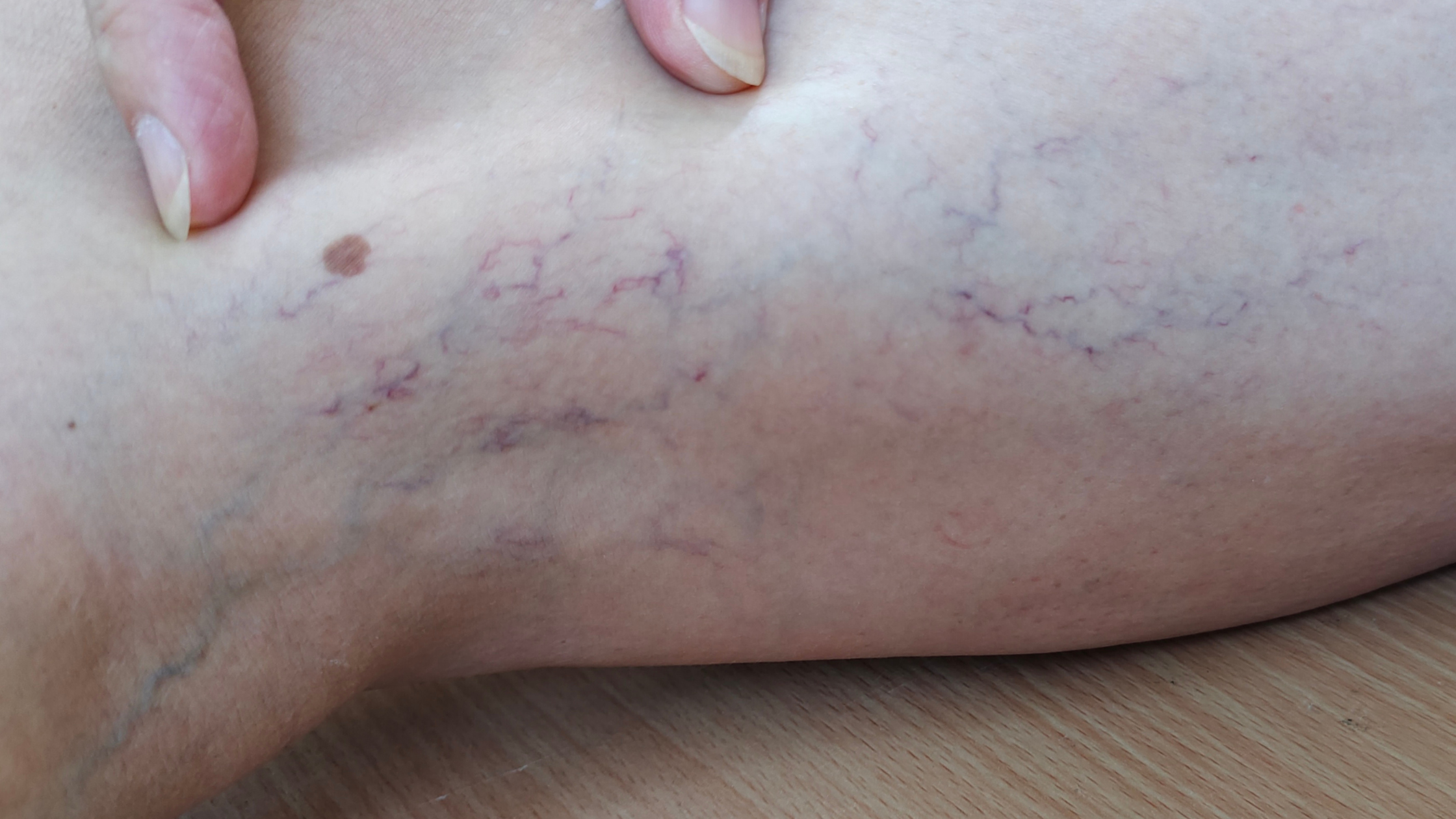
Millions of people across globe suffer from the prevalent disorder varicose veins. Usually showing just under the skin, these swollen, twisted veins usually affect the legs and can cause pain, swelling and discomfort. Though most people view varicose veins as a cosmetic issue, they can cause more major problems including hemorrhage. Varicose vein bleeding, sometimes referred to as venous hemorrhage, results from vein thin walls rupturing under stress or higher pressure. This disorder calls quick attention and can be concerning. This article will go over, how to manage and stop varicose vein bleeding successfully.
Understanding Varicose Vein Bleeding
When the valves in a varicose vein weaken or fail, blood pools and the veins enlarge. The rising pressure over time may cause the veins to become brittle and prone to rupture. After mild trauma, such a leg bump or skin scratch, varicose vein bleeding sometimes results. But given the significant weakening of the vein walls, it can also occur naturally.
Usually painless, varicose vein bleeding can be quite distressing and disruptive. Being deoxygenated blood from the veins, the blood could seem dark red or purple. Untreated, too much bleeding may cause major blood loss and problems.
Preventing Varicose Vein Bleeding
Preventing varicose vein bleeding includes addressing the fundamental reasons of varicose veins and thereby lowering the risk of harm to the impacted areas. These sensible actions help to reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight strains the veins in your legs, raising your chance of varicose veins and bleeding. Keeping a good weight by means of a balanced diet and consistent exercise helps to lower this pressure and enhance circulation.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity include swimming, cycling or walking increases good blood flow and builds the muscles supporting your veins. Steer clear of extended standing or sitting since this can cause blood to pool in the legs.
- Elevate Your Legs: Several times a day, elevating your legs above heart level for 15 to 30 minutes will help improve circulation and lower vein pressure. Additionally helping with varicose vein discomfort and swelling is this easy habit.
- Wear Compression Stockings: Compression stockings are specifically engineered to exert gentle pressure on the legs, enhancing blood circulation and preventing blood from accumulating in the veins. These are especially advantageous for those who engage in prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Compression stockings are meticulously crafted to exert gentle pressure on the legs, enhancing blood circulation and preventing the accumulation of blood in the veins. They are especially advantageous for those who spend prolonged periods in a standing or seated position.
- Protect Your Skin: The skin covering varicose veins tends to be thin and delicate, increasing its vulnerability to injury. Please refrain from scratching or bumping the affected area, and consider utilizing protective clothing or padding if deemed necessary.
- Stay Hydrated: Maintaining proper hydration is essential for ensuring healthy blood viscosity and circulation. It is advisable to consume an adequate amount of water daily to promote optimal vascular health.
- Seek Medical Treatment for Varicose Veins: See a healthcare provider for suitable treatment choices if you have notable varicose veins. Varicose veins can be removed and the risk of consequences including haemorrhage lowered by treatments including sclerotherapy, laser treatment or vein stripping.
Treating Varicose Vein Bleeding
Varicose vein bleeding can still strike in spite of preventative efforts. Minimizing blood loss and avoiding problems depend on knowing how fast and precisely to react. Should varicose vein bleeding strike you, here is what to do:
- Stay Calm: Although witnessing bleeding can be alarming, it is essential to maintain composure. Bleeding from varicose veins is generally not life-threatening when managed in a timely manner.
- Apply Direct Pressure: Using a clean cloth or sterile gauze, immediately apply firm, direct pressure to the bleeding point. To enable the blood to clot, keep pressure for at least ten to fifteen minutes. Steer clear of lifting the cloth to examine the cut since this will disturb the clotting mechanism.
- Elevate the Affected Leg: When applying pressure, ensure that the affected leg is elevated above heart level. This procedure effectively decreases blood circulation to the region and limits the occurrence of bleeding.
- Clean and Dress the Wound: To avoid infection once the bleeding has stopped, carefully wash the area with mild soap and water. Apply an antibiotic ointment then cover the cut with a sterile bandage or dressing.
- Seek Medical Attention: One should see a medical practitioner even if the bleeding stops. They can assess the degree of the bleeding, write appropriate prescriptions and counsel further activities to prevent recurrence.
- Consider Emergency Care: See emergency medical attention right once if bleeding is severe, does not stop after 15 minutes of direct pressure, or causes vertigo, fainting or signs of shock.
Medical Treatments for Varicose Veins
To reduce the risk of recurrent bleeding and tackle the root cause of varicose veins, it may be essential to pursue medical treatments. Some common options include:
- Sclerotherapy: Injecting a solution into the afflicted vein causes it to collapse and finally fade in this least invasive approach. Smaller varicose veins and spider veins respond well to sclerotherapy.
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT): By sealing off the afflicted vein with laser radiation, EVLT guides blood flow to healthier veins. This operation has a short recovery period and is carried out under local anesthesia.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Radiofrequency ablation closes off the injured vein using heat, much as EVLT. For bigger varicose veins, this is a safe and successful procedure.
- Vein Stripping: In more severe instances, it may be necessary to surgically remove the affected vein. This procedure is generally conducted under general anesthesia and necessitates an extended recovery period.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: This outpatient procedure entails the removal of smaller varicose veins via small incisions in the skin. This procedure is frequently conducted alongside additional therapies.
- Compression Therapy: Compression therapy could be advised as a long-term management plan for those not eligible for invasive treatments.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Management
In addition to medical treatments, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage varicose veins and reduces the risk of bleeding. Consider the following tips:
- Exercise Regularly: To boost circulation, do low-impact exercises include swimming, yoga or walking.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: To help vascular health, include foods high in antioxidants, flavonoids and fiber.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking adversely affects blood vessels and prevents circulation, worsening the condition of varicose veins.
- Monitor Your Symptoms: Watch any changes in your varicose veins—such as more swelling, pain, or skin changes—then let your doctor know.
Conclusion
Bleeding from varicose veins is a serious complication that necessitates immediate attention. Implementing preventive measures, including maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and utilizing compression stockings, can significantly lower the risk of bleeding and other complications. In the event of bleeding, it is crucial to apply direct pressure, elevate the leg, and seek medical attention to manage the situation appropriately.
See a healthcare practitioner to discuss treatment choices catered to your need for long-term management. Varicose veins can be minimized and comfortable, legs kept by correct treatment and lifestyle changes. Recall that early intervention is essential for both avoiding issues and enhancing your quality of life.