- admin
- 0 Comments
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition that involves the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, more probably in the thighs or the legs. Deep vein thrombosis if uninterrupted may result in serious complications such as a pulmonary embolism where the thrombus moves into the lungs and threatens the patient’s life. It is very important both to make understand the symptoms of DVT and to know what needs to be done in order to avoid it. This paper outlines how DVT can be detected, what risk factors may trigger this condition and how to prevent it.
Recognizing the Symptoms of DVT
To avoid complications of DVT, it is imperative that DVT diagnosis and treatment be sought as early as possible. Here are a few of the most common:
Swelling in One Leg
DVT’s usually occur in one leg causing a unilateral swelling which might develop within a few hours. With such swelling, one may experience heaviness to the affected leg or discomfort.
Pain or Tenderness in the Leg
The same blood clot that occludes the vein in DVT causes pain in the leg. In most cases, DVT related pain will start in the calf or thigh and will present itself as clamping, soreness or tenderness. Standing, walking or pointing the toes place more strain on the calf causing more pain to the affected leg.
Red or Purple Skin
Swelling and clotting may present with redness or bluish skin around the affected area. The abnormality in coloration is due to the failure of blood circulation to that particular region.
Increased Temperature to the Low Extremities
DVT is such that the affected leg will have more heat than the other skin. This is a result of inflammation as a consequence of the clot.
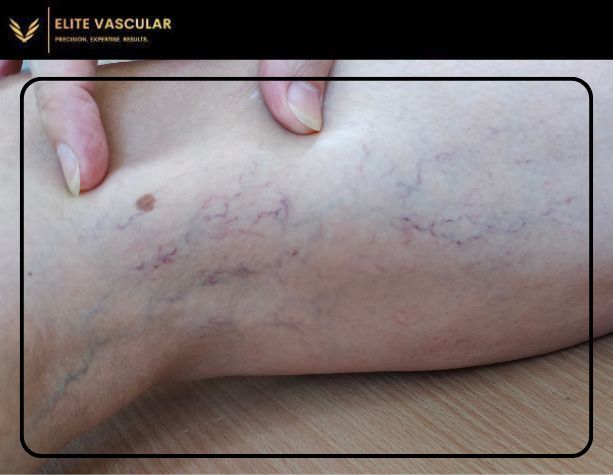
Swollen Bluish/ Red Veins
Some of the time blood vessels that lie superficially under the skin appear bigger and engorged than normal due to blood clipping. These symptoms some people notice even when there is no DVT, with DVT other complications are endangering such as pulmonary embolism (PE).
Such symptoms usually appear due to the underlining issues obstructed to heal DVT. If any of the above symptoms tend to progress then Immediate external assistance is needed to help the person where it is stabilizing the patient’s condition otherwise the patient’s progression will cease.
Deep vein thrombosis – Causes
Deep vein thrombosis is curable and can affect everyone, but some factors predispose a person to its development, among them risk factors are three. These are:
Generally immobile
Sitting for lengthy hours during international travel while on an aero plane shower rides long distance or going to bed post-surgery has also been known To increase risk in other words clot formation in the legs especially.
Surgery or Injury
Osteosynthesis and disarticulation methods of treatment involve serious surgery. The most troublesome for the vascular system are the relocations of the joints and the operations on the legs or pelvis. Such surgical operations can lead to alterations in the normal blood flow and in turn pose a risk of thrombosis. Damage of tissues including the blood vessels also results in deep venous thrombosis.
Medical Conditions
Some diseases such as cancer, heart failure, and inflammatory bowel disease should not be excluded from the list of the risk factors of the disease. A personal or a family history of blood clots is also another increase of the risks.
Hormone Therapy or Birth Control Pills
The use of hormone based medications, like birth control pills with estrogen or even hormone replacement therapy could carry risks for clotting.
Pregnancy
When pregnant there is increased pressure within the leg veins which made the pregnant women at increased risk for DVT. Even for several weeks after delivery the risk is still high.
Smoking
Cigarette use has long been known to damage blood vessels as well as impair blood circulation. Thus, they are also prone not only to DVT but also to other vascular disorders.
Age
It is quite clear that the risk for developing DVT increases with age mainly after the age of 60. It can develop at any age especially in individuals who have other risk factors.
Obesity
Increased weight tends to force body fluid on the veins of the legs thereby slowing up the movement of blood and encouraging blood clots in the process.
DVT Prevention: Their Best Practices
The good news is that there are proper measures that can be undertaken in order to prevent the blood clotting process in the legs. Here are some strategies to help prevent it:
Stay Active
Doing exercises continuously helps in enhancing healthy blood circulation which helps in minimizing chances of blood clotting. When you are sitting for long hours, for example when traveling, try and get up every hour and move a little. Even simple exercises like foot flexes and ankle circles can help.
Wear Compression Stockings
Products like compression stockings might be useful in enhancing the blood flow in the legs. They are primarily recommended for DVT patients.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
People who are regulated to obesity are at a higher risk of encountering DVT, hence weight control through proper dieting and exercises can prevent blood clots from forming.
Quit Smoking
Smoking enhances DVT risks in two ways, first by injuring the blood vessels and secondly by restricting normal blood delivery. This reverses the vascular health changes caused by smoking and reduces DVT potential.
Go for a Walk During the Day
Apart from all that pressure, this is the easiest preferable solution. To avoid sluggish circulation and swelling or bulk patchiness, activity, fresh air and getting up once in a while helps even without neglecting the other aspects of the solution.
Continue Compression Therapy if Prescribed
Your doctor or any other healthcare provider will most likely advise taking medications alongside the therapy. Also, continuous pressure clothing can assist the patients through a top-down pressure therapy or additional bottom-up compression.
Maintain Activity While Traveling
On returning, and to prevent DVT, the patients are encouraged to be active, that is to reclaim their previous pre-surgery endeavors or even new ones, as guided by a practitioner. In most cases, it performed CDRs, high compliance of ankle dorsiflexion was restored.
Stand and Walk Periodically
On medication, gradual activity should be introduced. It is also recommended during treatment to wear compression devices due to the vascular hypertrophy. Meditation can then appropriately be recommenced.
Preventing DVT with the help of Final Thoughts: Recognition
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious health condition if left untreated. There are some warning signs to this and the risks may be quite manageable. Such actions as engaging in physical activities, controlling one’s weight, and using compression stockings can minimize the chances of DVT.
If you have a DVT condition or are likely to develop one, get in touch with a physician for an appropriate diagnosis and management. Taking precautions against the development of more severe health issues is possible through early diagnosis and correction.