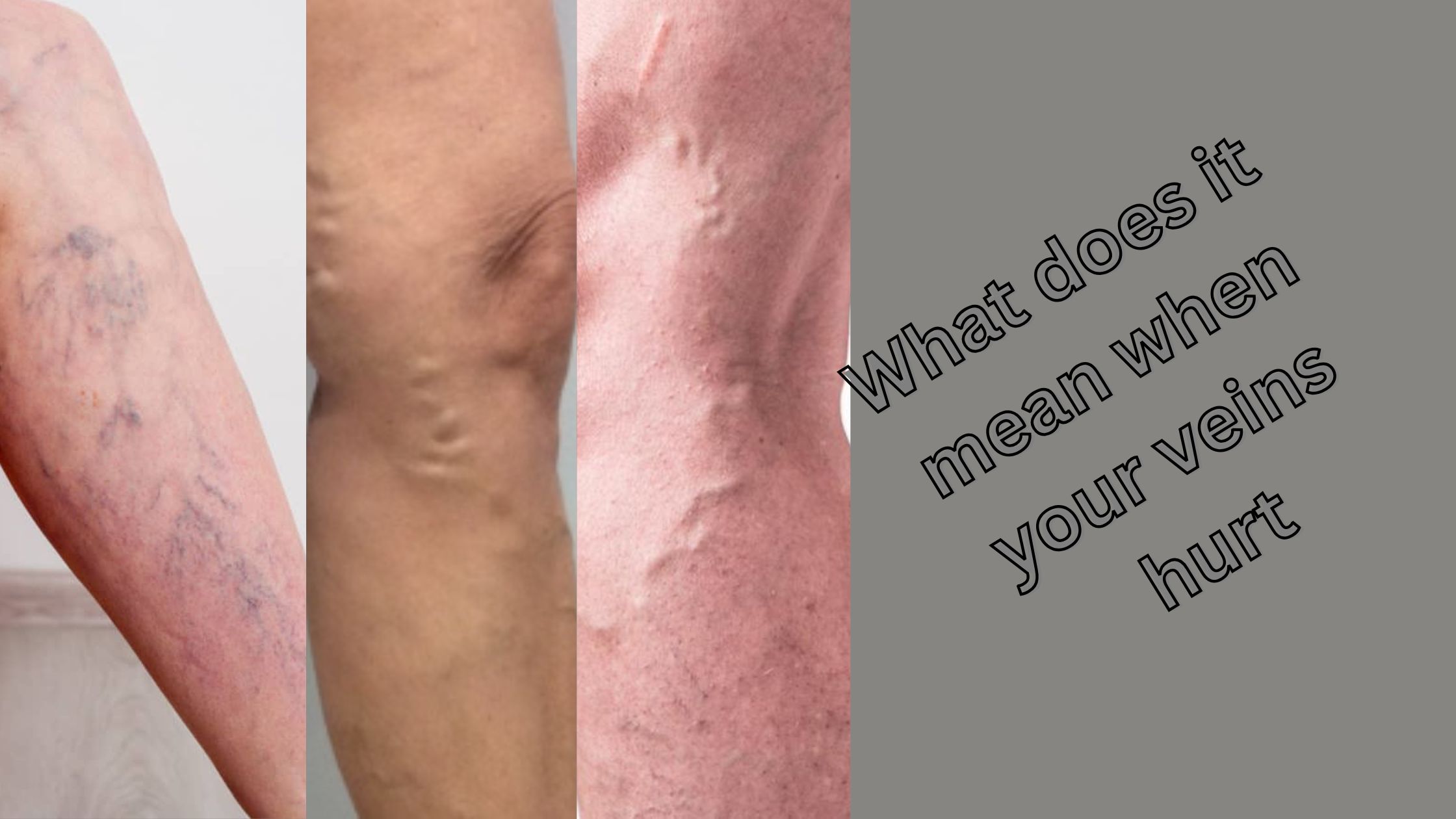
Pain in the vein can be a dangerous and uncomfortable feeling (sensation), which is often described in the form of throbbing, pain, or irritation in the passage (path) of the veins. Although sometimes inconvenience (discomfort) is not serious, persistent or severe pain in the nerves can be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires attention.
In this detail article, we will discuss when the possible causes of vein pain, related symptoms, risk factors and when to seek medical help.
Understanding Vein Pain: Who does it feel like?
Pain in the veins usually occurs in the legs, hands or other areas where the veins are close to the skin. General details include:
- Heaviness and pain, especially in the legs
- Throbbing or pulsating discomfort
- Burning or itching around the vein, Tenderness to touch
- Swelling or redness along the vein
If you experience these symptoms, it is important to identify the possible cause immediately and consult with your healthcare provider.
Common Causes of Vein Pain
Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are swollen, folded veins that often appear blue or purple. They occur when the weak or damaged vein valves allow blood to pooling, which increases the pressure and hurts (pain).
Symptoms:
- Bulging, rope-like veins, Leg cramps
- Pain increases (worsening pain) after standing/sitting for a long time
Treatment:
- Compression stockings
- Sclerotherapy (injections to close veins)
- Laser therapy or vein stripping (for severe cases)
Phlebitis (Vein Swelling)
Phlebitis occurs when the vein occurs swelling (inflamed), often caused by injury, infection, or prolonged use of IV. There are two types:
- Superficial phlebitis (it affects veins near the skin)
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition involving deep veins (blood clots), most commonly occur in the legs but also in arms and pelvic area
Symptoms:
- Red, warm, tender vein
- Swelling along the vein
- Possible fever (if infected)
Treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory medications, Warm compresses
- Antibiotics (if infection is present)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
DVT (deep vein thrombosis) is a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs. This is a medical emergency because clot can travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism (PE).
Symptoms:
- Sharp or cramping pain, Swelling in one leg
- Skin discoloration (red or blue)
- Warmth over the affected area
Treatment:
- Blood thinners (anticoagulants)
- Thrombolytics (clot-dissolving drugs), Compression therapy
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Although Pad affects the arteries, it can cause similar pain. Low (reduced) blood flow causes muscle cramps and discomfort, which is often understood to be vein pain.
Symptoms:
- Leg pain while walking (claudication)
- Cold or numb feet, Slow-healing wounds
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes (quitting smoking and exercise also helps)
- Medications for improving blood flow, surgery if necessary in severe cases.
Venous Insufficiency
This condition arises when the veins struggle in bringing blood back to the heart, due to which blood gets pooled and pressure arises.
Symptoms:
- Swollen ankles, Itchy or flaky skin
- Leg ulcers (in advanced cases)
Treatment:
- Elevating legs, Compression therapy
- Minimally invasive procedures (For example, RFA (radiofrequency ablation)
Superficial Thrombophlebitis
Blood clot in superficial vein causes inflammation and pain. Unlike DVT, it is less dangerous but still inconvenient (uncomfortable).
Symptoms:
- Hard and tender vein
- Redness and warmth, Mild swelling
Treatment:
- Pain relievers (NSAIDs)
- Warm compresses, Monitoring for complications
Injury or Overuse
Straining muscles or bruising near veins can cause localized pain.
Muscle stretch (straining) or injury (bruising) near the veins can cause localized pain.
Symptoms:
- Bruising, Soreness with movement
- Temporary swelling
Treatment:
- Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE method)
- Pain relievers
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical help if you experience:
- Immediate, severe leg pain with swelling (possible DVT, deep vein thrombosis)
- Chest pain or breathing difficulties (sign of pulmonary embolism, PE)
- Fever with red, swollen veins (infection risk chances)
- Non-healing wounds or skin changes
Preventing Vein Pain Tips
- Stay active (walking/exercise improves circulation)
- Avoid prolonged sitting/standing (take break every hour)
- Wear (compression stockings) if you are at risk
- Stay hydrated to prevent blood clots(drink enough water daily)
- Keep a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the veins (eat healthy balanced diet)
Final Thoughts
Pain in the veins should never be ignored, especially if it (along with) is swelling, redness or heat (warmth). While some reasons are minor, such as muscle stretch, others (such as DVT) require immediate care. Initial diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve the health of the veins. If you are regularly experiencing the vein discomfort (pain), consult with your healthcare provider instantly for proper assessment and personalized treatment options.