- admin
- 0 Comments
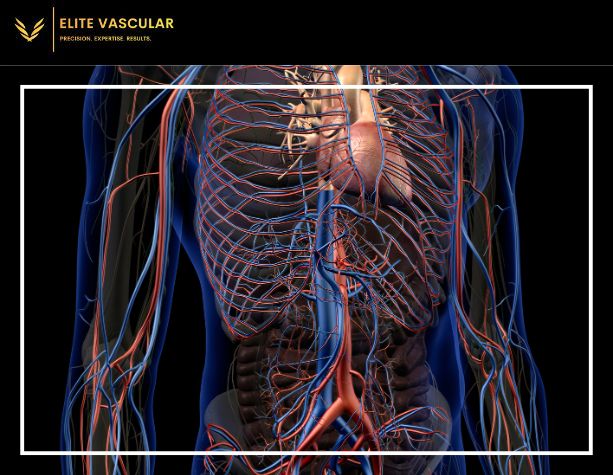
The circulatory system is made up of arteries and veins which are important for transportation of blood throughout the body. The different colors of arteries and veins, red and blue respectively have always been interesting to people. This distinction in color has led to the question why are arteries red while veins blue? The article goes into depth about this issue by exploring scientific explanations behind these differing pigments in blood vessels as well as shedding some light on principles such as oxygenation of blood, absorption and reflection of light.
Basics of Blood Circulation
Before getting into detail about colors associated with each type it is necessary to know what they do within our bodies:
Arteries
Arteries are responsible for carrying oxygen rich-blood from heart to other parts of human body. The largest artery known as aorta branches off into smaller ones that reach different organs and tissues.
Veins
Veins bring back deoxygenated or oxygen-poor blood towards the heart again. From there it gets pumped into lungs where it gains more oxygen before repeating this process all over again.
Oxygenation & Blood Color
The main cause for difference between arterial and venous colours can be attributed to their respective levels of oxygen content:
Blood Rich In Oxygen (Red)
Arterial blood contains high amount of oxyhaemoglobin which gives bright-red colour when viewed under normal circumstances . This vibrant shade arises because O₂ combines with haem groups altering molecular structure together with light absorbing properties.
Low levels Of O₂ (Blue)
Once delivered to cells organs etc venous supply becomes depleted thus having more deoxyhaemoglobin that has dark bluish-red color instead. Veins appear blue if you look at them through your skin because they absorb scatter light differently than arterial does so.
Light Absorption & Reflection
How we see hue in veins depends on how our skin interacts with these vessels vis-a-vis rays coming from sun:
Skin – Light Relationship
Skin absorbs different wave lengths of light unevenly by causing it to scatter more some areas than others. Blue is scattered more by fat tissues when compared to red because shorter wavelength which penetrates deeper into subcutaneous layer before dispersing through other parts like muscle or bone where longer ones are absorbed faster.
Perceiving Vein Color
When you look at a vein beneath your epidermis, the rays that have managed passing through bounce back into our eyes giving us perception of its color . More blue scatters thus reflects back as opposed to red hence veins appear bluish even if blood inside them is dark red.
Why Aren’t Arteries Seen As Blue?
Veins are usually close to skin surface while arteries lie deep within human body so they can hardly be seen with naked eye. Moreover, arterial blood being richly saturated in oxygen has bright-red appearance therefore any artery situated near derma may still look reddish or blackish due high concentration of oxyhemoglobin filled in it.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
There are many misconceptions surrounding this topic but here are few examples:
Myth: Blood Is Blue Inside Veins
Fact: Blood never appears blue regardless of whether it’s in veins or elsewhere. Venous supply just happens to contain darker shade than arterial one though both shades fall under range called “red”. So what makes them seem different then? It has everything do with optics
Myth: Dark-red Blood Is Always Devoid of Oxygen
Fact: Even though dark-red blood indicates that it is low in oxygen, it still contains some redness. The blackness depends on the amount of saturation with oxygen but never entirely lacks redness.
Factors that Affect Visibility of Blood Vessels
There are several factors which can affect how we see and interpret the color of blood vessels through our skin:
Complexion
Complexion or skin tone plays a major role in determining how clearly we see veins. People with lighter complexions may see their veins as blue because blue light is scattered while those with darker ones may not notice them easily or perceive them as different colors altogether.
Fatty Tissue
The presence of subcutaneous fat affects absorbance and scattering of light thereby changing the visibility of veins. Thinner individuals tend to have more visible veins.
Advancement in Age
With advancing age, our skins become thinner exposing more veins which leads to changes in what we consider their color.
In conclusion,
The coloration of arteries and veins is a captivating combination between biological principles and optics knowledge. Arteries are red since they carry highly oxygenated blood while veins look blue beneath the skin due to light absorption and scattering properties Understanding this distinction helps us understand better about our bodies’ circulation system as well as debunking misconceptions about blood colors Knowing these factors will enable one appreciate the intricate nature and aesthetics of human physique.